Managing Microservices Timeouts

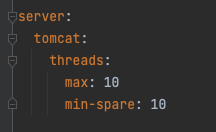
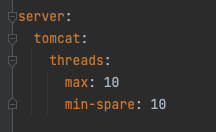
Context: Services request timeout is usually something that is less scrutinized over when designing a solution. Which is rightly so if we are considering a simple solutons (1-2 daisy chained microservices), and/or monolith ones. However that changes when we start looking at 5+ daisy chained microservices, as the diagram below illustrate it Fig 1. All microservices have the same timeouts Now one could argue that we could obtain baseline of how long on average Microservice 5 will take to process the request and generate a response and configure each of the microservices accordingly, such as follow: Fig 2. Each microservices slightly higher timeouts than downstream Which indeed would work well under a straight forward, theoritical happy case scenario. However most experienced SREs would agree that what matter is not the happy case scenario, but how the system handle all sort of stress loads. Even if we can come up with the golden number for the baseline of Microservice 5, this approa...